- Home
- breathing patterns
- Spontaneous Breathing Patterns of Very Preterm Infants Treated With Continuous Positive Airway Pressure at Birth
Spontaneous Breathing Patterns of Very Preterm Infants Treated With Continuous Positive Airway Pressure at Birth
5 (160) · $ 12.50 · In stock
Very Preterm Infants Failing CPAP Show Signs of Fatigue Immediately after Birth
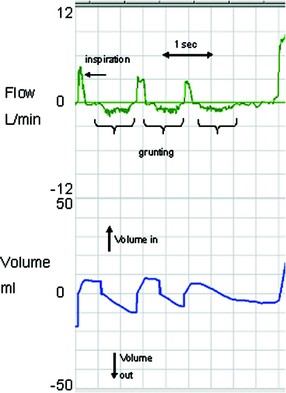
Breathing Patterns in Preterm and Term Infants Immediately After Birth
Monitoring Lung Aeration during Respiratory Support in Preterm Infants at Birth

Aerosol drug delivery to spontaneously-breathing preterm neonates: lessons learned, Respiratory Research
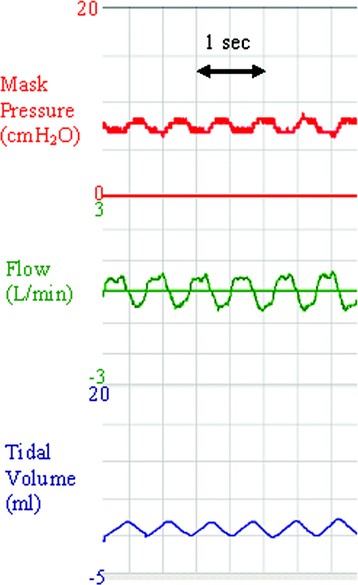
Spontaneous Breathing Patterns of Very Preterm Infants Treated With Continuous Positive Airway Pressure at Birth

Application of two different nasal CPAP levels for the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants—“The OPTTIMMAL-Trial”—Optimizing PEEP To The IMMAture Lungs: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial, Trials
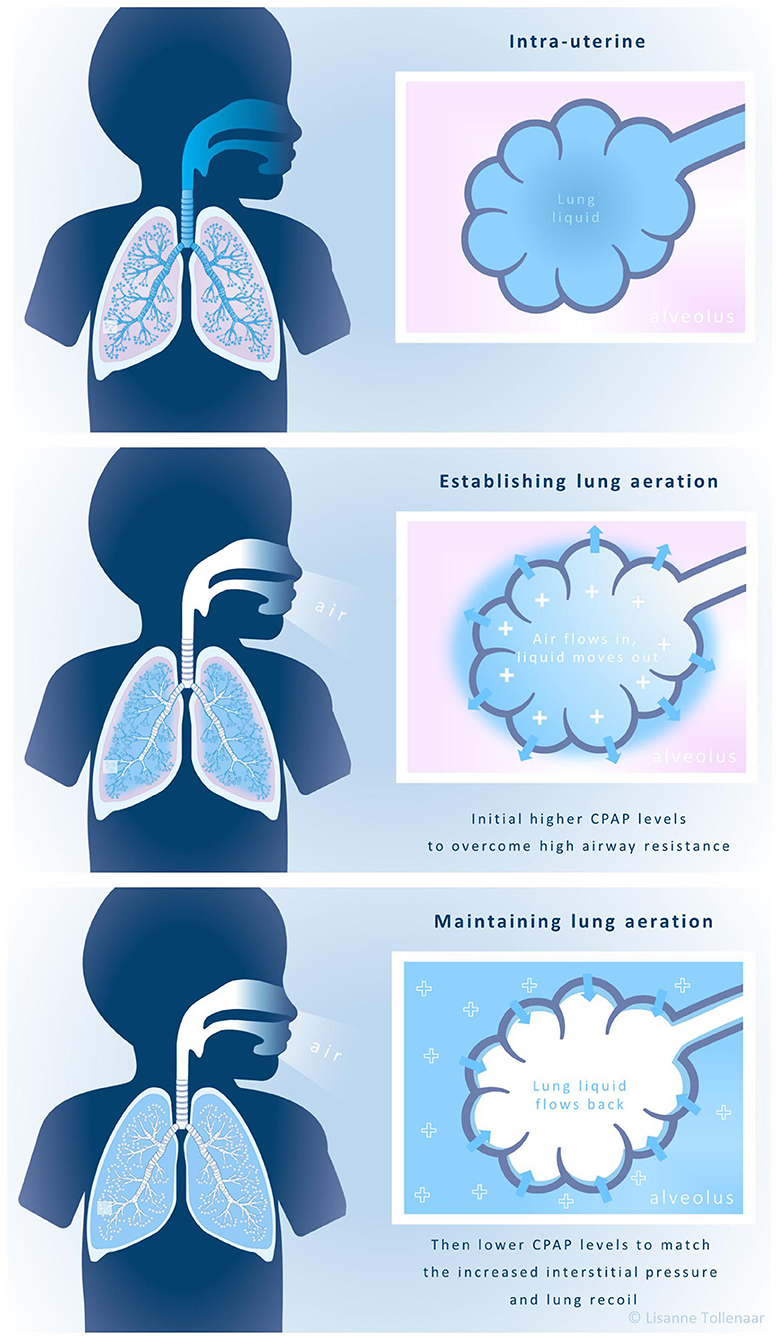
Frontiers Feasibility and Effect of Physiological-Based CPAP in Preterm Infants at Birth
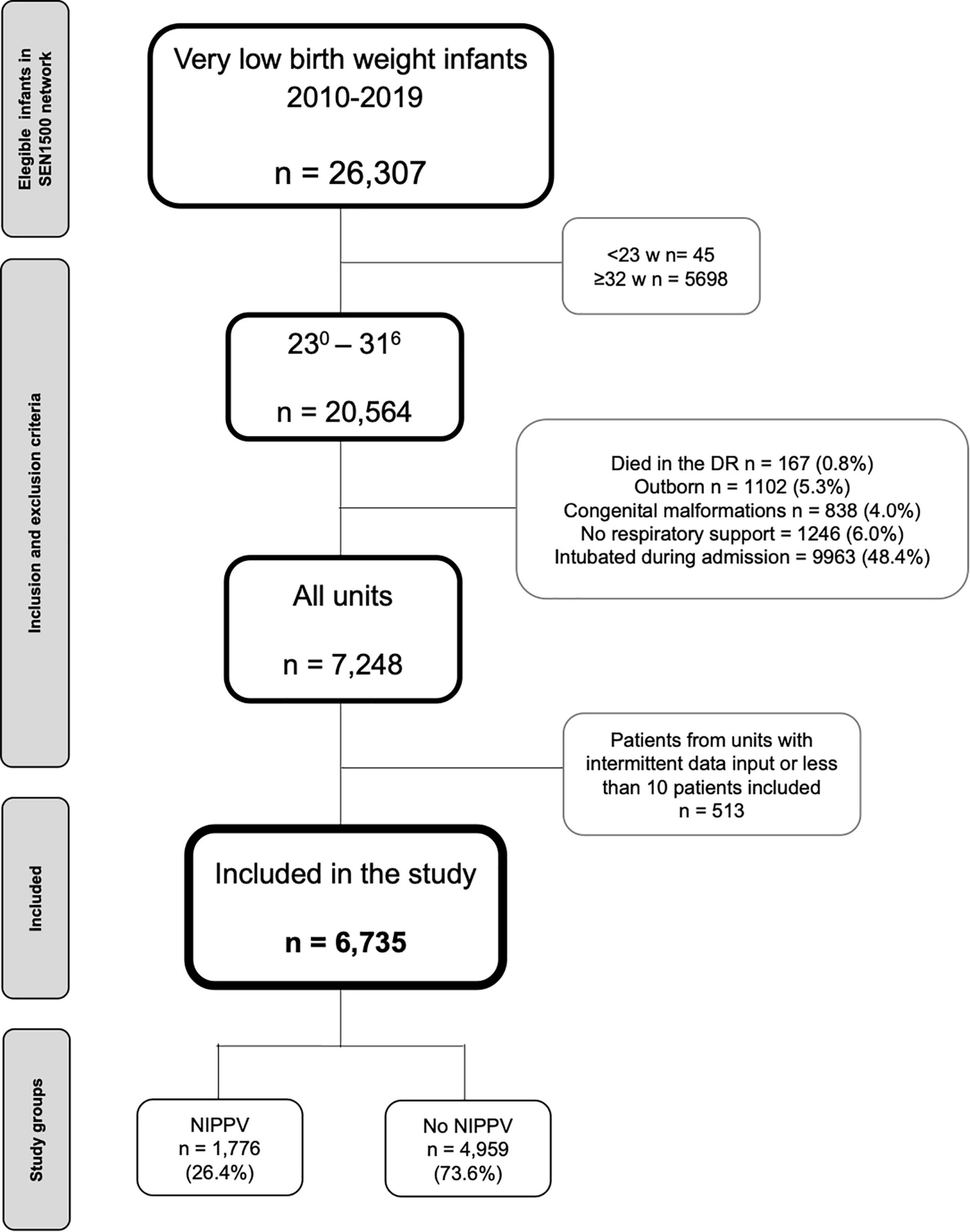
Frontiers Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Among Very Preterm Infants Never Intubated During the First Neonatal Admission: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)

Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation in infants with upper airway obstruction: comparison of continuous and bilevel positive pressure

Mask ventilation of preterm infants in the delivery room
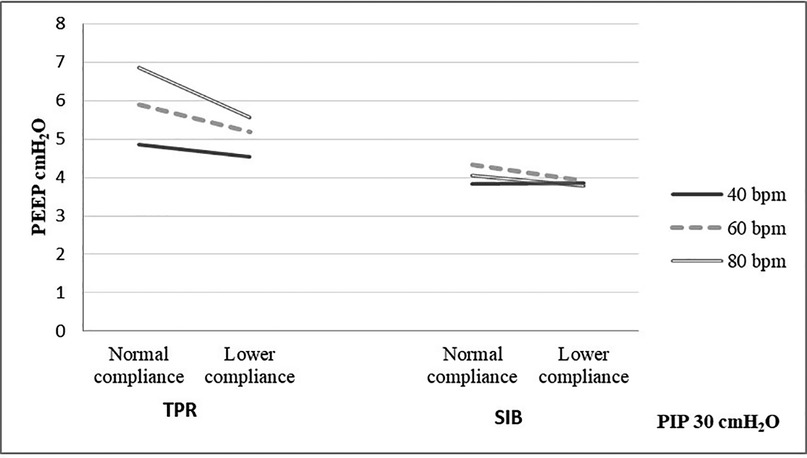
Frontiers Positive end expiratory pressure and respiratory system resistance between self-inflating bag and T-piece resuscitator in a cadaveric piglet lung model

Higher versus lower nasal continuous positive airway pressure for extubation of extremely preterm infants in Australia (ÉCLAT): a multicentre, randomised, superiority trial - ScienceDirect

Establishing lung gas volumes at birth: interaction between positive end-expiratory pressures and tidal volumes in preterm rabbits
The Administration of 100% Oxygen and Respiratory Drive in Very Preterm Infants at Birth