- Home
- convert 36.5 c to fahrenheit
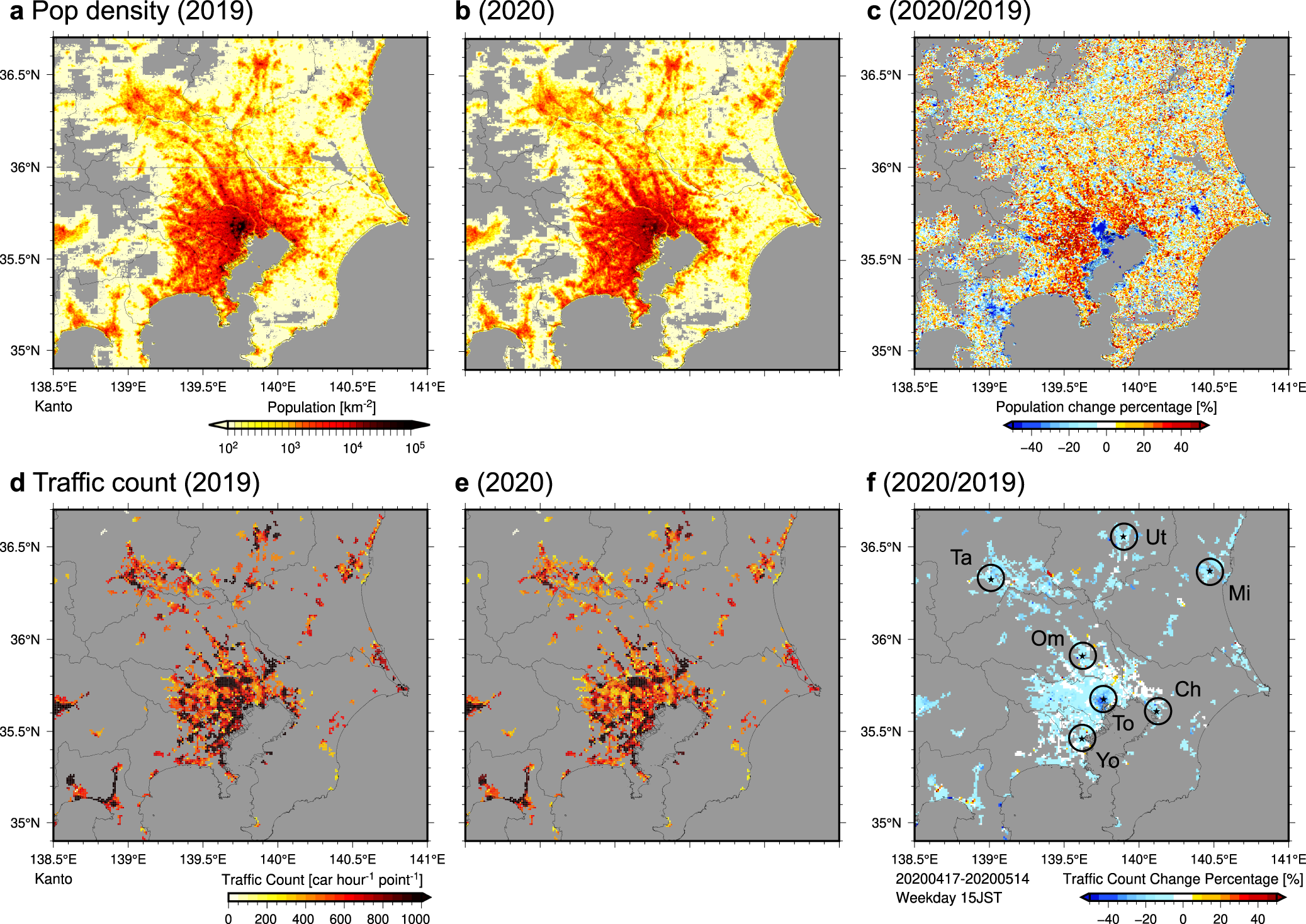
- Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data
Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data
4.9 (561) · $ 24.50 · In stock

Spatially heterogeneous effect of temperature on electricity consumption in Shenzhen, China - ScienceDirect
Influence of human population movements on urban climate of Beijing during the Chinese New Year holiday

NH3 emissions from the human body in central Tokyo decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown - ScienceDirect

Spatial distribution of August monthly mean surface air temperature

Mean four-week, 1st October–28th October 2014, traffic volume at a

Times sequence (from 1Z to 23Z) showing the zonal average (10°W–10°E)

Improvement of WRF–CM–BEM and its application to high-resolution hindcasting of summertime urban electricity consumption - ScienceDirect
COVID-19-induced low power demand and market forces starkly reduce CO2 emissions

Hourly settings of Q fs on weekdays for the O urban grids. The settings
Urban Climate Changes During The COVID-19 Pandemic:, 48% OFF
Global urban climatology: a meta-analysis of air temperature trends (1960–2009)

Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data

Meteorological statistics for all days (x), clear-sky days (circles)